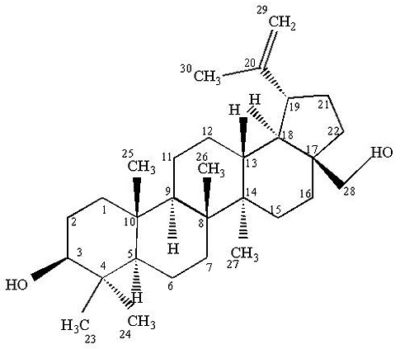
A precursor of betulinic acid is a triterpene found in the bark of the Betula alba (white birch) tree
- Catalog No: APH-02011
- CAS Number: 473-98-3
- Chemical Formula: C30H50O2
- Molecular Weight: 442.73
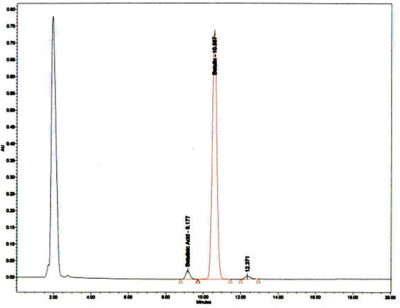
- Purity: > 95% determined by HPLC
- Appearance: White to off-white crystalline solid
- Solubility: Poorly soluble; soluble in DMSO (50 mM)
- Stability: Solids stored at 5°C should be stable up to 1 year. Stock solutions stored at -20ºC should be discarded after 1 month unless retesting confirms product quality.
- Storage: 5°C
- Shipping: Ambient
- Handling: Nominal
Source:
Betulin, a non-bioactive precursor of betulinic acid, is also found in the bark of the Betula alba (white birch) tree at concentrations of up to 25%. The tree is fast-growing and abundant in North America and Europe. The raw material is readily available in large quantities since birch bark is considered a waste product in the pulp and paper, and furniture manufacturing industries.
Aphios manufactures betulinic acid and betulin from Betula alba bark utilizing its patented SuperFluids™ CXP technology. Betulin is then purified using chromatography techniques.
Betulinic acid can be manufactured from betulin in a 2-step semi-synthetic process with an overall yield of approximately 71%.
Biological Activity:
In an animal study, researchers found betulin from birch bark lowered cholesterol, obesity and improved insulin resistance (Song, 2011).
Scientists have studied betulin in mice, and they found that the ingredient that is abundant in birch bark lowered cholesterol and improved insulin sensitivity. They also found the mice became more resistant to plaque buildup in the arteries that can lead to heart attack.
References:
Song B. (2011). Cell Metabolism. Vol. 13, Issue 1, pp. 44-56.