The primary active constituent of marijuana (Cannabis sativa) responsible for its psychoactive and medicinal properties
- Catalog No: APH-02021
- CAS Number: 1972-08-3
- Chemical Formula: C21H30O2
- Molecular Weight: 314.47
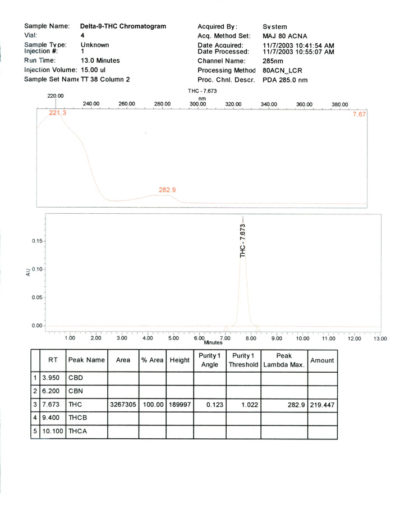
- Purity: > 99% CP HPLC
- Appearance: Slightly colored ethanolic solution
- Solubility: Soluble in methanol and ethanol
- Stability: Δ9-THC is very unstable, decomposing rapidly in the presence of oxygen and light. It appears to be more stable in ethanol and methanol than as a solid.
- Storage: -20°C
- Shipping: On ice (5°C)
- Handling: Avoid exposure to oxygen and direct sunlight.
Source:
While Δ9-THC can be synthesized, the process is complex and expensive. Synthetic Δ9-THC (Dronabinol) was first manufactured in the United States by Norac, Inc., Azusa, CA, which had an exclusive supply agreement with Unimed Pharmaceuticals for use in its Marinol® product, a preparation of synthetic Dronabinol dissolved in sesame oil. Several generic versions of Dronabinol from pharmaceutical companies are currently on the market.
At Aphios, Δ9-THC is extracted from the flowers and buds of Cannabis sativa(marijuana) utilizing patented SuperFluids™ CXP technology [Castor, US Patent] followed by segmentation chromatography to complete the purification of natural pharmaceutical grade Δ9-THC for medical use.
Biological Properties:
Δ9-THC is considered the primary active constituent responsible for the psychoactive and medicinal properties of marijuana.
A select number of the 65 cannabinoids, including Δ9-THC, the medically active component of C. sativa, hold the promise of providing new drugs for a variety of treatment purposes. The use of Cannabis for medical treatments has the legal disadvantage that distribution of the plant material to patients violates US Federal law. Smoking Cannabis has the medical disadvantage that the smoke contains many toxic components in common with tobacco smoke, and delivers a highly variable dose of Δ9-THC and other cannabinoids.
Marinol® is approved by the US FDA as an appetite stimulant for HIV/AIDS patients and as an antiemetic to stem the nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy. Oral administration of Marinol®causes slow, variable Δ9-THC uptake, because the oil-based capsule can be difficult to digest, especially in patients suffering nausea from chemotherapy.
Natural cannabinoid products directly isolated from the plant C. sativa are being developed to treat pain in cancer patients and cachexia or wasting in AIDS patients, and provide relief to Alzheimer’s patients while increasing their appetite.
There are also currently very high levels of activity in the clinical evaluation of cannabinoid active ingredients and derivatives. In fact, many theoretical and early-stage clinical opportunities for cannabinoid therapy are well-developed, with a wide range of indications previously or currently in clinical evaluation.
Marijuana is the most popular and widely used illicit drug among young adults. More than half of US young adults will experiment with Cannabis. The National Survey on Drug Abuse and Health reports that more than 100 million of the US population aged 12 and older has tried marijuana at least once.
Although most young adults use Cannabis occasionally and for recreational purpose, some use Cannabisrepeatedly and for prolonged periods of time. The Drug Abuse Warning Network estimates that more than 215,000 emergency visits each year are due to marijuana use. NIDA estimates that around 300,000 people entering drug treatment programs reported marijuana as their primary drug of abuse.
References:
Joy J, Watson S and Benson J (Eds.). (1999). Cannabis and Medicine: Assessing the Science Base. Institute of Medicine. National Acad. of Sciences: Washington, DC.
National Institutes of Health. (1997). Workshop on the Medical Utility of Cannabis. Report to the Director of NIH by the Ad Hoc Group of Experts.